摘要
SpaceX announced a plan for a bold, innovative, new approach to land a human crew on Mars. Unlike traditional space missions that minimize mass, the SpaceX approach utilizes many lower-cost launches to create a simplified, robust mission concept utilizing large amounts of mass.
SpaceX claims it will land a crew on Mars in the next several years.
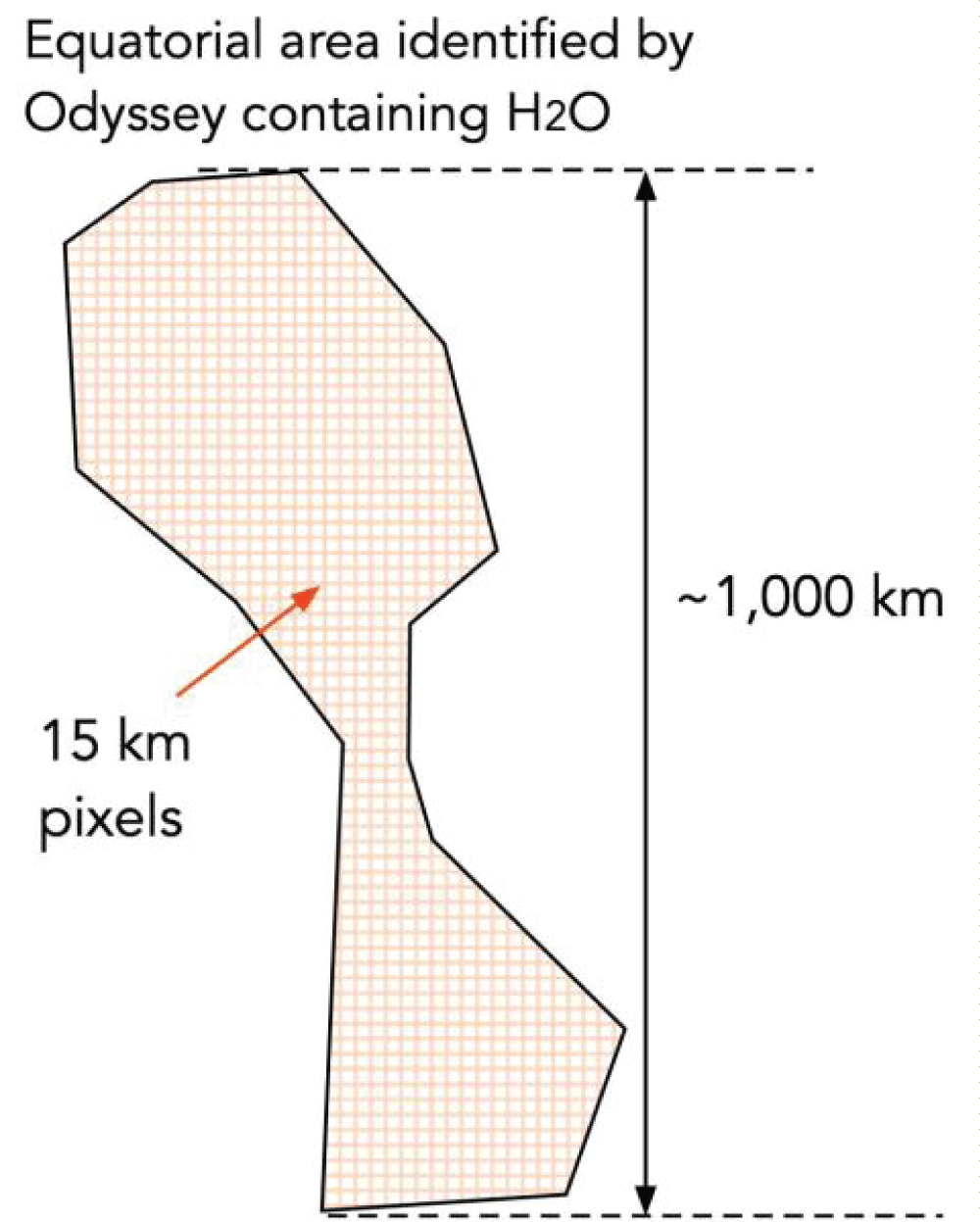
A great deal of development and validation in situ of critical elements of the mission must be demonstrated prior to carrying out the mission. The in situ production of 1,200 MT of cryogenic propellants and the entry descent and landing of a 200 MT vehicle represent the greatest challenges. Locating an accessible source of H2O at a suitable landing site will require a series of launches of prospecting missions at increasing resolution at 26-month launch intervals.
The preparation for the ultimate SpaceX mission will require at least ten years and most likely twenty years of development and demonstration at a cost of several tens of billions of dollars. It is not clear why SpaceX continues to make bold claims for timing that is not possible.




![Map of water content in the upper 1 m of the Mars surface as estimated from modeled measurements taken by the gamma ray spectrometer on the Odessey orbiter. Light blue areas have significantly less hydrogen than dark blue areas [14]. This figure is modified from Butcher (2022) [12].](https://www.igminresearch.cn/articles/figures/igmin292/igmin292.g001.png)